Some of the links in this post are affiliate links. This means if you click on the link and purchase the item, I will receive an affiliate commission at no extra cost to you.
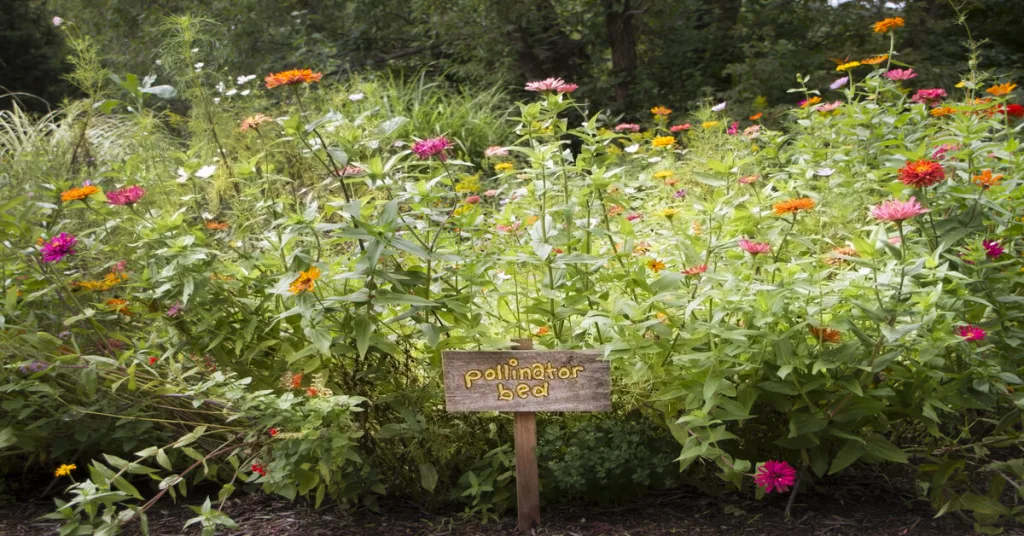
Pollinator gardens are special gardens designed to attract pollinators. These pollinators include bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds.
These gardens are an important resource for the environment. They play a vital role in the reproduction and survival of many plant species.
One subset of pollinator gardens is a butterfly garden. These pollinator gardens provide nectar-rich plants that attract and support butterflies in particular.
No matter the size or style, pollinator gardens provide critical habitat for pollinators. They also help to ensure the health and diversity of our ecosystem.
You can even start your own pollinator garden to benefit the environment. Follow the steps below to learn more.
What is a Pollinator Garden?

A pollinator garden is a type of garden designed to attract and support pollinators. Pollinators include animals such as bees, butterflies, hummingbirds, and other insects.
Pollinators are important because they help plants to reproduce and bear fruit.
Pollinator gardens often include plants that bloom at different times. This provides a continuous source of nectar and pollen.
These gardens may also include features such as water sources and nesting sites. These help support the basic needs of pollinators.
Pollinating gardens provide valuable habitats for pollinators. They also are a beautiful and educational addition to any landscape.
Pollinator Garden Benefits
Pollinator gardens provide a variety of benefits to the environment, including the below:
- Promotes biodiversity. Pollinator gardens support a wide variety of pollinators. This helps increase the biodiversity of an area. The gardens also provide a source of food for pollinators.
- Combats declining pollinator populations. Pollinator habitats have been destroyed or altered significantly over the years. This has caused the pollinator population to plummet. Pollinator gardens help reverse this trend.
- Helps produce crops and fruit. Pollinators are essential for the production of many fruit-bearing crops.
- Provides a beautiful and educational space. Pollinator gardens help people learn about the importance of pollinators.
- Reduces the use of pesticides. Pollinator gardens can help to reduce the need for pesticides. Pollinators help feed on pests.
A pollinator garden is a beneficial experience for both people and the environment.
Disadvantages of Pollinator Gardens
There are a few potential disadvantages to pollinator gardens.
One disadvantage is that pollinator gardens need regular maintenance. This includes watering, weeding, and pruning, which can be time-consuming.
Another disadvantage is that pollinator gardens may attract other pests. Common pests include aphids or spiders.
Finally, pollinator gardens may not be suitable for all locations. Certain plants may not thrive in certain climates or soil types.
How to Build a Pollinator Garden

Building a pollinator garden is easy. Follow the steps below to get started.
- Choose a location for your pollinator garden. Look for a spot that gets at least six hours of sunlight a day and has well-draining soil.
- Make a plan. Decide what types of plants you want to include in your garden and where you want to place them. Consider the size and shape of your garden. Check on the needs of the plants and pollinators you want to attract.
- Time your garden. Start pollinator gardens in the spring or fall. The weather is cooler and there is more moisture in the soil. This helps plants get established and grow strong roots before the hot summer. If you live in a more mild climate, you can start plants throughout the year.
- Prepare the soil. Remove any weeds and loosen the soil with a garden fork. Add compost or other organic matter to help improve the soil structure and fertility. Remove any weeds that pop up.
- Plant your flowers, trees, and shrubs. Follow the instructions on the plant labels for proper spacing and care. Be sure to include a variety of plants that bloom at different times throughout the year. This provides a continuous source of food for pollinators.
Purchasing seedlings will be quicker than seeds, but seedlings are usually more expensive. Opt for native species over invasive plants. Plant in clumps, as this attracts more pollinators over single plants.
- Add some water. Pollinators need access to water. Consider adding a small pond, birdbath, or another water source to your garden.
- Keep an eye on your garden and make necessary adjustments. Water and fertilize your plants as needed. Avoid synthetic fertilizers with high nitrogen content. These fertilizers promote leafy growth at the expense of flowers.
Avoid the use of pesticides. They may kill pollinators and other beneficial insects.
- Sit back and enjoy! As your pollinator garden grows and matures, it will become a haven for all sorts of pollinators. Expect to see bees, butterflies, hummingbirds, or other creatures in your garden.
Best Plants for Pollinator Gardens
There are many plants that are great for attracting pollinators to your garden. Some options include:
- Flowers: Popular choices include lavender, sunflowers, daisies, cosmos, zinnias, marigolds, coneflowers, and foxgloves. Usually, any type of flowering plant will work.
- Herbs: Good options include basil, mint, rosemary, thyme, oregano, and cilantro. They are great for attracting bees, butterflies, and other predatory insects. Borage also improves soil fertility while attracting pollinators.
- Fruit trees: Apple, cherry, peach, apricot, and plum trees provide food for pollinators.
- Shrubs: Blueberries, raspberries, blackberries, and lilacs are also great for pollinators.
- Peas and beans: Legumes produce small, colorful flowers. These flowers attract bees and other insects. They also make great companion plants by adding nitrogen to the soil.
- Native plants: Many native plants are great for attracting pollinators. Some examples include milkweed, butterfly weed, and native grasses.
It is important to research the specific needs of the plants you want to include in your garden. Make sure they are suitable for your location.
Most Common Pollinators Found in the Garden
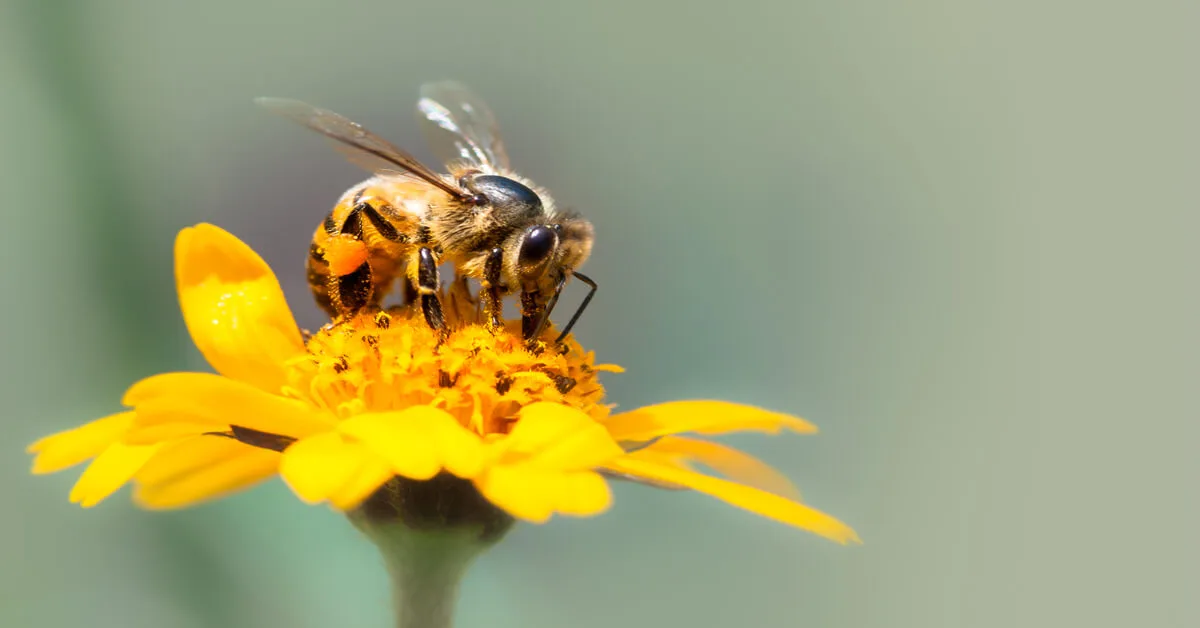

Here is a list of the most common pollinators found in gardens:
- Bees: Honey bees, bumblebees, and solitary bees are all important pollinators.
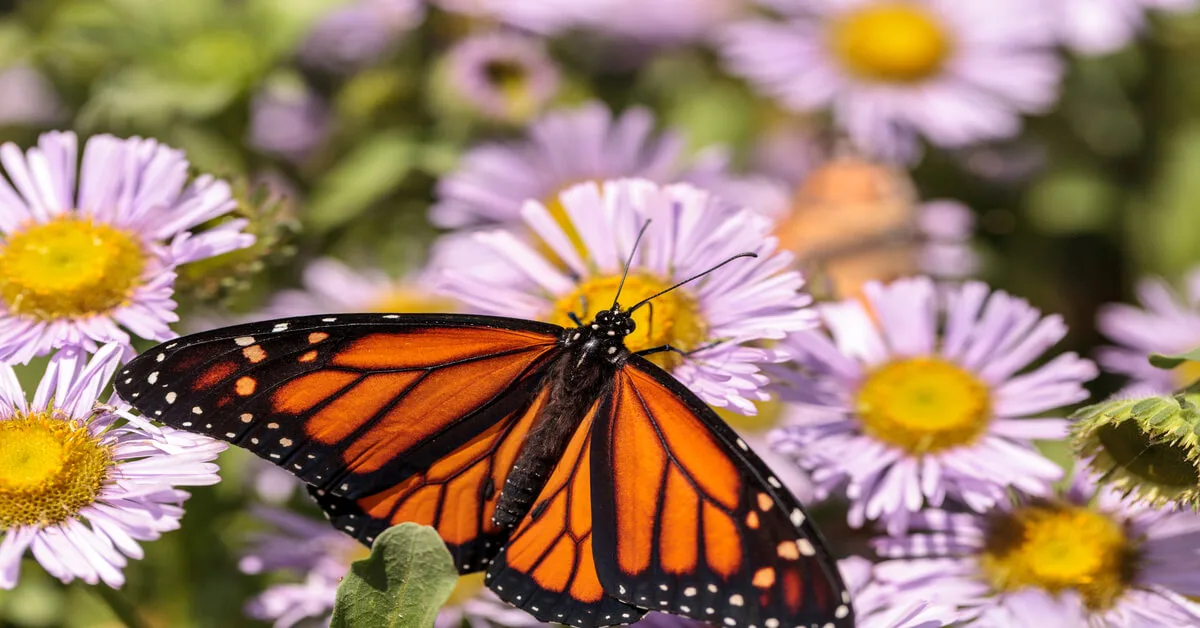
- Butterflies: There are many species of butterflies that help to pollinate plants. Butterflies prefer a wide variety of flowers.
- Hummingbirds: These small, energetic birds feed on nectar from flowers. They serve as important pollinators.
- Beetles: Some species of beetles are important pollinators. They like flowers with strong scents.
- Wasps: Many species of wasps are important pollinators. Wasps are especially important for plants that bloom later in the season.
- Flies: Some species of flies are important pollinators. Examples include hoverflies and syrphid flies.
- Moths: Some species of moths are important pollinators for plants that bloom at night.
It is important to provide a variety of plants that bloom at different times. This will attract a wide range of pollinators to your garden.
Interest in Pollinator Gardening
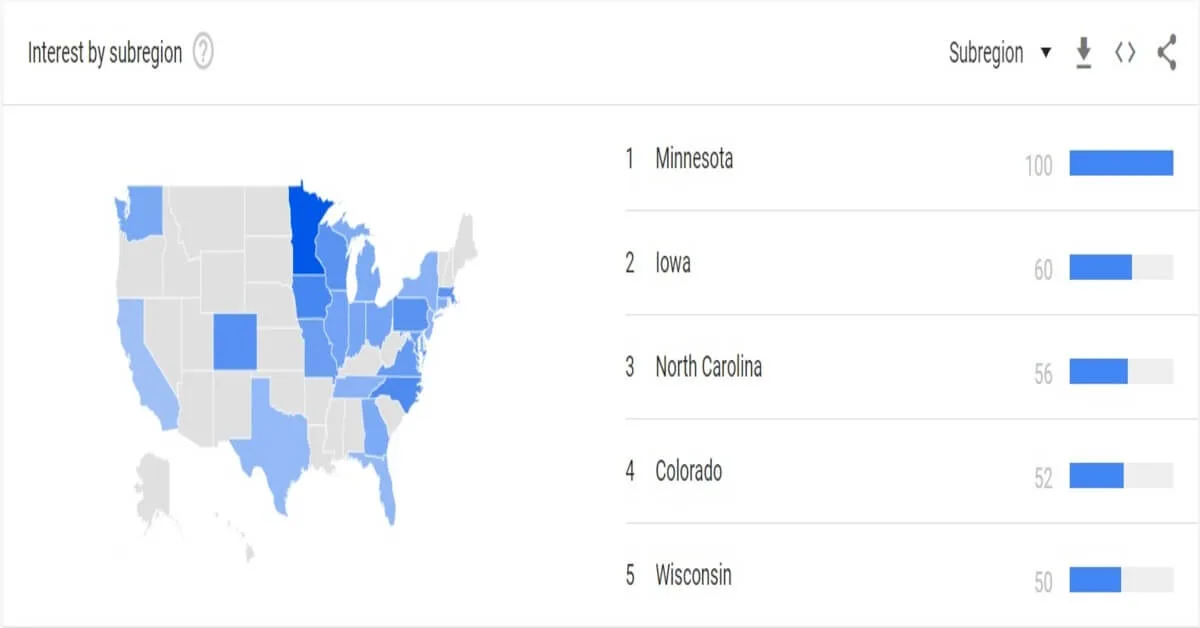
According to 2022 Google Trends, Minnesota, Iowa, North Carolina, Colorado, and Wisconsin are states with the highest level of interest in pollinator gardens.
Minnesota has the highest level of interest in pollinator gardens. The state has implemented many initiatives to support pollinator conservation. A “lawns to legumes” grant encourages residents to plant flowering legumes over lawns. [1]
Iowa ranks second. The state has implemented many pollinator-friendly initiatives. Examples include a plan to plant pollinator-friendly flowers along highways.
North Carolina, Colorado, and Wisconsin have also implemented a variety of pollinator initiatives.
Which are Better Pollinators: Bees or Butterflies?
Bees and butterflies are important pollinators. They play a vital role in the health of our ecosystems and food production.
Bees are important pollinators for a wide variety of plants. Bees help pollinate flowers, vegetables, and fruit trees. There are many species of bees. Each species will have its own specific preferences and behaviors.
For example, honey bees are social insects that live in large colonies. Honey bees help pollinate crops such as fruit. Bumblebees are also important pollinators. They help pollinate plants that bloom later in the season. Solitary bees, such as mason bees, are important pollinators for many native plants.
Butterflies are also important pollinators. They prefer a wide variety of flowers. Butterflies love bright-colored flowers with strong scents, such as roses and lilies. Unlike bees, butterflies are able to see red. [2]
Butterflies are less efficient than bees in moving pollen. Instead, their long, thin bodies and tongues allow them to reach nectar in deep or narrow flowers.
It is important to provide a variety of plants that bloom at different times. This helps attract a wide range of pollinators to your garden.
Our Recommended Resources
Wildflower 50,000 Bulk, 1 Bag
Wildflower Seeds Butterfly and Humming Bird Mix
References:
[1] Musgrave, R. (nd). Pollinator Protection Policy Options 2021. National Caucus of Environmental Legislators.https://www.ncelenviro.org/resources/pollinator-protection-policy -options-2021/.
[2] Unknown authors, (nd). Butterfly Pollination. U.S. Forest Service. https://www.fs.usda.gov/wildflowers/pollinators/animals/butterflies.shtml.

